Unmasking the Threat: Understanding the Health Risks of Smoking. Articles are written about the dangers of smoking, TV shows are made, posters are printed, and scary pictures with the consequences of tobacco use are placed on cigarette packs. However, only a few people give up their bad habits.
Most smokers continue to poison the body, not paying attention to the warnings of the Ministry of Health. WHO compares smoking to a terrible epidemic. In Russia, 60% of men and 25% of women are regular tobacco users. From year to year, the Russian Federation is among the ten most smoking countries in the world. In this article, we will tell you how smoking affects your health, what nicotine is, and why it is so difficult to give it up. Also, read expert advice on how to overcome tobacco addiction.
Deadly consequences of smoking
Risks of smoking also Cigarettes contain nicotine, chemical additives, and aromatic impurities. When it all starts to burn, tobacco smoke is released, which the smoker swallows. The composition of the smoke is a deadly mixture containing the following substances:
More risks of smoking are Potent poisons – arsenic and cyanide. Ammonia is an aggressive irritant for mucous membranes. Cytotoxins that poison the body at the cellular level. Based on them, chemotherapy drugs are made to kill cancer tumors. Carbon monoxide (about 2%). This is dangerous carbon monoxide, which binds to hemoglobin when released into the blood. As a result of the interaction, carboxyhemoglobin is formed in red blood cells, which cannot carry oxygen. Carcinogens (in toxic resins).
Firstly, nitrosamines, which destroy brain structures. Secondly, benzopyrene and benzopyrene are dangerous substances that cause cancer and genetic mutations. In addition to the mentioned carcinogens, tobacco smoke contains formaldehyde, hydrazine, chrysene, urethane, and almost fifty other similar substances that can activate cancer cells, integrate into DNA, and damage the genome. Radioactive elements.
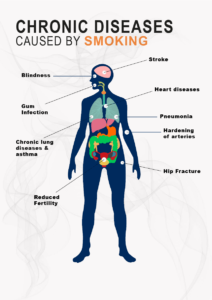
The most dangerous are soft metals—polonium, lead, and bismuth. They interfere with biochemical processes, affect the liver, kidneys, and heart, cause the death of blood cells, and cause irreversible changes in the nervous system. In addition to the destructive impact on one’s health, a smoker causes harm to others. People who inhale smoke from passive smoking receive a whole range of dangerous substances. Over time, the risk of smoking, poisons, and carcinogens accumulate in the body, causing chronic diseases.
How does smoking affect the oral cavity?
Teeth and gums suffer from bad habits no less than internal organs. C combustion products settle on the enamel with each puff, becoming a dense coating on the gingival margin and tooth crown. Mixing with microparticles of tissue detritus and food debris, specific deposits create a favorable environment for the proliferation of cariogenic bacteria that destroy hard enamel and detritus. Poisons penetrate the tooth through the resulting microcracks, poisoning the interdental tissues.
Smoke dries the oral mucosa and increases its sensitivity under the influence of nicotine; the capillaries that supply the gums with nutrients narrow. Due to low tropism, gum tissue weakens and atrophies. Periodontal pockets form, into which infection easily penetrates. Over time, teeth become loose, crumble, and fall out.
Due to constant exposure to tar, smokers’ tooth enamel quickly demineralizes, turns yellow, and becomes covered with dark spots. Even whitening toothpaste cannot restore the white color of teeth.
 Risks of smoking on the respiratory system
Risks of smoking on the respiratory system
Smoking is inhaling tobacco smoke, which damages the larynx and lungs. Once in the respiratory tract, toxic resins glue the protective villi (cilia), opening the way for harmful substances. They are absorbed into the lung tissue, destroying its structure, which leads to the formation of infiltrates. Lung tissue becomes denser, and the area of gas exchange decreases.
Nicotine addiction causes:
- emphysema;
- pneumosclerosis;
- chronic inflammation of the bronchial tree and lung tissue;
- tuberculosis;
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease);
- malignant tumors of the upper and lower respiratory tract.
The larynx contains the vocal cords, which are responsible for phonation. With the systematic impact of combustion products on the mucous membrane, the ligaments lose elasticity, become loose, and swollen.
With passive smoking, the immunity of the mucous membranes decreases. The hypopharynx becomes more vulnerable to viral and bacterial infections. The accumulation of toxic substances during systematic inhalation of tobacco smoke causes chronic diseases of the throat and bronchopulmonary system.
Risks of smoking for developing cancer
Scientists have long proved the pathogenetic connection between tobacco addiction and oncology. The level of risk depends on nicotine experience, the age of the smoker, and the number of cigarettes consumed. The higher the indicators, the more likely the development of malignant processes. According to the localization of tumors, lung and larynx cancer ranks first. The risks of smoking factor for people who smoke 14-15 cigarettes per day is 7,9. Those who smoke up to 24 cigarettes have 12,7. When compared with non-smokers, these figures are 10-20 times higher.
The leading types of malignant neoplasms are squamous cell and small cell carcinoma. Smoking becomes the main cause of lung cancer in 90% of sick men and 55-85% of sick women. About 60% of malignant neoplasms of the larynx are caused by nicotine addiction.
The second place in cancer statistics among smokers is cancer of the digestive and urinary systems. The risks of smoking factors for non-smokers increases by 5 times (cancer of the esophagus and bladder), 3 times (cancer of the pancreas and liver), and 1.5 times (cancer of the stomach and kidneys).
The effect of smoking on the psyche
Nicotine addiction is considered by many to be not as serious as drug and alcohol addiction. The development mechanism is the same. The health consequences are similar. The only difference is that ethanol and prohibited substances destroy a person quickly, and nicotine acts in slow motion. However, it does no less harm. Once hooked on nicotine, a smoker gets two addictions at once – psychological and physical. Initially, a psychological craving is formed (as a kind of situational ceremony).
For example, smoke after eating, while waiting for transport, or when meeting friends. Gradually, ritual smoking breaks turn into a persistent habit formed with the participation of the central nervous system. And this is already an addiction on a physical level when a cigarette becomes needed for a temporary improvement in well-being.
Tobacco leaves and stems contain the main “hook” for smokers – the alkaloid nicotine, which acts on n-cholinergic receptors – acetylcholine nicotinic receptors in the brain. When irritated, these receptors lead to a state of excitation of parts of the parasympathetic nervous system, which are associated with the work of the heart, blood vessels, and gastrointestinal tract.
Nicotine affects the neurotransmitter dopamine, which, along with serotonin, is responsible for feelings of pleasure. During smoking, dopamine transmission changes, causing the brain to experience pleasurable sensations.
Due to the direct effect on the central nervous system, the craving for cigarettes becomes stronger with each puff. After some time, nicotine is integrated into the dopamine system and becomes part of it. Alcohol acts similarly, becoming entrenched in metabolic processes. When addiction is formed, the level of dopamine is regulated by tobacco consumption. To maintain a comfortable concentration of the neurotransmitter, the addict increases the number of cigarettes smoked and reduces the intervals between smoke breaks.
If there is no opportunity to smoke, dopamine levels drop, and the smoker begins to experience withdrawal symptoms. Dry mouth, increased sweating, digestive problems, irritability, insomnia, and emotional swings appear.
Electronic cigarettes are no less dangerous in terms of developing addiction. Most of them contain the same amount of nicotine as regular ones (about 6-7 mg). At the same time, vapes often use not a natural tobacco substance but artificially synthesized nicotine sulfate. Previously, it was used in agriculture as a pesticide to combat plant diseases and harmful insects.
How to quit smoking?
The TOP 6 traditional smoking cessation tips include:
- Finding motivation. You need to find a reason so that the bonuses outweigh the need for nicotine. Some psychologists recommend undergoing a medical examination. Any person obsessed with smoking will show signs of premature aging and disturbances in the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, and bronchopulmonary system. If health improvement and appearance transformation are not motivating, a desired purchase or trip with saved money can be an incentive.
- Uniting like-minded people. It is very difficult to quit smoking alone. Breaking a bad habit will be much easier if you encourage dependent relatives and friends. You can arrange a competition and create a prize (possibly cash).
- Cleansing space. After you decide to quit, you need to remove all smoking-related items from your home: throw away ashtrays, cigarette holders, and lighters. Washing all clothes and treating upholstered furniture and carpets saturated with smoke is also advisable.
- Medicinal assistance. You should not ignore modern medications against nicotine addiction. They work on the principle of nicotine replacement therapy – they help to survive withdrawal symptoms without discomfort. You can use any convenient pharmacological form – patches, sprays, lozenges, Nicorette chewing gum, etc. Traditional healers advise taking decoctions of medicinal herbs that suppress the desire to smoke (valerian, hops, skullcap, lemon balm).
- Switching interests. Medicines help overcome physical dependence. To overcome psychological cravings, experts advise replacing smoking breaks with reading, watching the news, physical exercise, and drawing. Of course, this is difficult, and it’s not for nothing that parting with cigarettes is called a “struggle.” It will take a lot of effort.
- Substitution. To ease psychological stress and not “break down” if you want to smoke, you can suck on caramels, sweets, bite nuts, and eat fruit. Roughly speaking, the brain calms down if the mouth is busy during a cigarette break.
Most heavy smokers rarely succeed in quitting the first time. It is important not to despair or give up but to repeat attempts until you defeat the dangerous habit completely.


 Risks of smoking on the respiratory system
Risks of smoking on the respiratory system